Gather the necessary tools for solving a chemistry problem. Having everything you need easily accessible will simplify the process of solving the assigned problem.
You will need the following:. A pencil and paper. Calculations are easier to solve when you write them out. Be sure to show all your steps to get full credit.
A periodic table. You will need to be able to find atomic weight of elements using the periodic table. A calculator. Calculators are necessary to simplify calculations of complex numbers. Identify the elements in the compound that you need to convert into moles. The first step in calculating molecular mass is identifying each element that composes the compound.
It is easy to distinguish elements because abbreviations contain only one or two letters. If a compound is abbreviated with two letters, the first will be capitalized while the second will be lowercase. For example, Mg is the abbreviation Magnesium. The compound NaHCO 3 has four elements in it: Sodium (Na), Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), and Oxygen (O). Determine the number of atoms that each element contributes to the compound.
You must know how many atoms of each element are present to calculate the molecular mass. The number of atoms each element contributes will be written in a subscript next to the element. For example, H 2O has two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. If a compound has parentheses followed by a subscript, each element within the parentheses gets multiplied by the number in the subscript. For example, (NH 4) 2S has two atoms of N, eight atoms of H, and one atom of S. Calculate molecular mass.
The molecular mass of a substance is calculated as the number of atoms of each element multiplied by the atomic weight of that element. Knowing the molecular mass is necessary to convert grams to moles.
Multiply the number of atoms each element contributes to the compound by the atomic weight of that element. Add the total weight of each element in the compound together. For example, (NH 4) 2S has a molecular weight of (2 x 14.01) + (8 x 1.01) + (1 x 32.07) = 68.17 g/mol.
Molecular mass is also referred to as molar mass.
Key Takeaways Key Points. The mole allows scientists to calculate the number of elementary entities (usually atoms or molecules ) in a certain mass of a given substance. Avogadro’s number is an absolute number: there are 6.022×10 23 elementary entities in 1 mole. This can also be written as 6.022×10 23 mol -1. The mass of one mole of a substance is equal to that substance’s molecular weight. For example, the mean molecular weight of water is 18.015 atomic mass units (amu), so one mole of water weight 18.015 grams. Key Terms.
mole: The amount of substance of a system that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12. The chemical changes observed in any reaction involve the rearrangement of billions of atoms. It is impractical to try to count or visualize all these atoms, but scientists need some way to refer to the entire quantity. They also need a way to compare these numbers and relate them to the weights of the substances, which they can measure and observe. The solution is the concept of the mole, which is very important in quantitative chemistry. Avogadro’s Number.
Key Takeaways Key Points. The molar mass is the mass of a given chemical element or chemical compound (g) divided by the amount of substance (mol). The molar mass of a compound can be calculated by adding the standard atomic masses (in g/mol) of the constituent atoms.
Molar mass serves as a bridge between the mass of a material and the number of moles since it is not possible to measure the number of moles directly. Key Terms. molar mass: The mass of a given substance (chemical element or chemical compound in g) divided by its amount of substance (mol).
mole: The amount of substance of a system that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12. Measuring Mass in Chemistry Chemists can measure a quantity of matter using mass, but in chemical reactions it is often important to consider the number of atoms of each element present in each sample. Even the smallest quantity of a substance will contain billions of atoms, so chemists generally use the mole as the unit for the amount of substance.
One mole (abbreviated mol) is equal to the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12; this number is referred to as Avogadro’s number and has been measured as approximately 6.022 x 10 23. In other words, a mole is the amount of substance that contains as many entities (atoms, or other particles) as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12. G/mol Each ion, or atom, has a particular mass; similarly, each mole of a given pure substance also has a definite mass. The mass of one mole of atoms of a pure element in grams is equivalent to the atomic mass of that element in atomic mass units (amu) or in grams per mole (g/mol). Although mass can be expressed as both amu and g/mol, g/mol is the most useful system of units for laboratory chemistry. Calculating Molar Mass Molar mass is the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of that substance, measured in g/mol.
For example, the atomic mass of titanium is 47.88 amu or 47.88 g/mol. In 47.88 grams of titanium, there is one mole, or 6.022 x 10 23 titanium atoms. The characteristic molar mass of an element is simply the atomic mass in g/mol. However, molar mass can also be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass in amu by the molar mass constant (1 g/mol). To calculate the molar mass of a compound with multiple atoms, sum all the atomic mass of the constituent atoms.
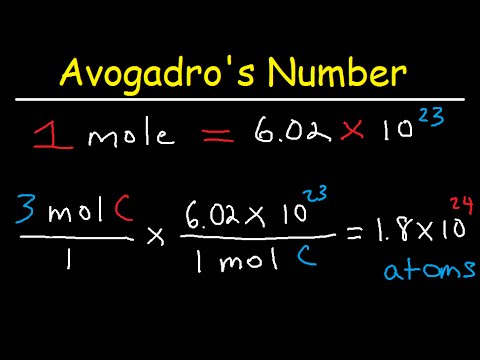
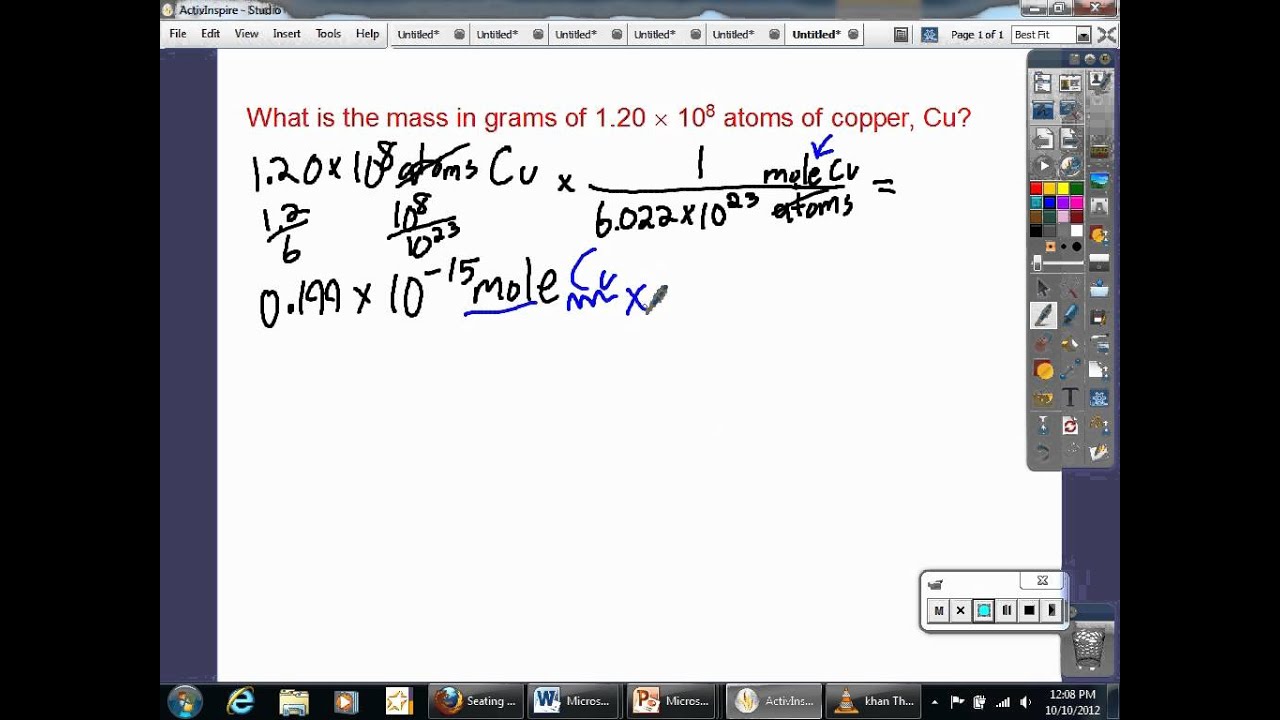
For example, the molar mass of NaCl can be calculated for finding the atomic mass of sodium (22.99 g/mol) and the atomic mass of chlorine (35.45 g/mol) and combining them. The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol. Key Takeaways Key Points. The molar mass of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of its constituent atoms in g/mol. Although there is no physical way of measuring the number of moles of a compound, we can relate its mass to the number of moles by using the compound’s molar mass as a direct conversion factor. To convert between mass and number of moles, you can use the molar mass of the substance.
Then, you can use Avogadro’s number to convert the number of moles to number of atoms. Key Terms. molar mass: The mass of a given substance (chemical element or chemical compound) divided by its amount of substance (mol), in g/mol.
dimensional analysis: The analysis of the relationships between different physical quantities by identifying their fundamental dimensions (such as length, mass, time, and electric charge) and units of measure (such as miles vs. Kilometers, or pounds vs. Kilograms vs. Grams) and tracking these dimensions as calculations or comparisons are performed. mole: The amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12.
Chemists generally use the mole as the unit for the number of atoms or molecules of a material. One mole (abbreviated mol) is equal to 6.022×10 23 molecular entities (Avogadro’s number), and each element has a different molar mass depending on the weight of 6.022×10 23 of its atoms (1 mole).
The molar mass of any element can be determined by finding the atomic mass of the element on the periodic table. For example, if the atomic mass of sulfer (S) is 32.066 amu, then its molar mass is 32.066 g/mol. By recognizing the relationship between the molar mass (g/mol), moles (mol), and particles, scientists can use dimensional analysis convert between mass, number of moles and number of atoms very easily. CC licensed content, Specific attribution. Avogadro's number and the mole.
Provided by: Steve Lower's Website. License:.
Mole (unit). Provided by: Wikipedia. License:.
Avogadro constant. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:. mole. Provided by: Wiktionary.
License:. The Mole, Avogadro.
License Terms: Standard YouTube license. Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. License:. Avogadro constant. Provided by: Wikipedia.
License:. mole. Provided by: Wiktionary. License:. Avogadro's number. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:.
The Mole, Avogadro. License Terms: Standard YouTube license. Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. License:.
Molar mass. Provided by: Wikipedia.
License:. Atomic mass unit. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:. molar mass. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:.
mole. Provided by: Wiktionary. License:. The Mole, Avogadro.
License Terms: Standard YouTube license. Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. License:. Molar Mass Calculations - YouTube. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
Avogadro's number and the mole. Provided by: Steve Lower's Website. License:. mole. Provided by: Wiktionary. License:.
Atoms To Mass In Grams Converter
molar mass. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:. Dimensional Analysis. Provided by: Wikipedia. License:. The Mole, Avogadro.
License Terms: Standard YouTube license. Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. License:. Molar Mass Calculations - YouTube.
License Terms: Standard YouTube license.